Guide to the EIC Accelerator challenges 2024
- Stéphanie

- Jun 10, 2024
- 8 min read
The European Innovation Council (EIC) was introduced by the European Commission to support the commercialization of high-risk, high-impact technologies in the European Union. Launched in March 2021 under the Horizon Europe program, it emerged from a pilot phase that began in 2018, incorporating existing instruments under the Horizon 2020 program, such as the SME instrument and Future & Emerging Technology (FET) program. The EIC plays a pivotal role in helping researchers, startups, and SMEs to bring their innovations to market by providing funding, networking opportunities, and business acceleration services

3 funding schemes adapted to your TRL: EIC Pathfinder, EIC Transition and EIC Accelerator
The European Innovation Council (EIC) structures its funding and support into three principal schemes. The EIC Pathfinder encourages advanced research to establish the groundwork for breakthrough technologies. Complementing this, the EIC Transition focuses on validating these technologies and crafting business models for their application. For more market-oriented goals, the EIC Accelerator supports companies, including SMEs, startups, and spin-offs, in commercializing and scaling their innovations. Two types of schemes are available within the EIC Pathfinder and Accelerator: "Open" calls for all technology fields, and targeted "Challenges" calls for strategically important areas. In this article, we will focus on the EIC Accelerator Challenges.
EIC Accelerator Challenges Topics
In 2024, the EIC Accelerator proposes to fund 6 challenges in specific areas:
The goal of this Challenge is to promote a European approach to AI that centers on human values, addressing key issues such as lack of transparency and trust. European AI startups are poised to create advanced generative AI models that reflect EU principles and ensure Europe's independence in this vital area.

Specific objectives:
Develop foundation language and multimodal 'frontier' capable of matching or surpassing the most advanced large generative models, designed to fulfill the requirements of European industries, researchers, public sector, and citizens.
Develop smaller foundation models that exhibit highly competitive performance in specific fields, challenging larger frontier models.
The developed models are expected to advance beyond the current technologies, addressing the existing challenges and limitations. Areas for potential enhancements include creating generative AI models that minimize fictional content for reliability and models that enhance transparency by allowing users to trace information sources.
The primary target for these developments are SMEs that either develop these models directly or provide essential infrastructure and tools supporting AI development. These companies must commit to embodying European values in their AI solutions, using this as a strategic advantage for competitiveness and investment security.
This Challenge focuses on enhancing high-fidelity virtual worlds for high-impact markets and applications, aligning with Industry 5.0 principles such as sustainability, human-centricity, and resilience. It seeks to scale up innovations in platforms, middleware, tools, and devices. The initiative also guides the integration of virtual world technologies into addressing Industry 5.0 Challenges, which span economic, ecological, and social aspects globally. The funding will support solutions that cater to industry demands for upskilled talent, resource efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reduced carbon emissions. These solutions aim to maximize the benefits of technologies by reducing costs, applying them to sustainability or resilience challenges, improving collaborative work environments and learning, and enhancing ergonomics.

Specific objectives: Support the development and deployment of advanced virtual worlds technology solutions for industry and in particular:
Development of AI-driven, human-centric agents to enhance interactions within virtual worlds, crafting adaptive environments and scenarios for more intuitive and accessible immersive experiences, particularly in dynamic Industry 5.0 contexts like innovation management and operations.
Utilization of this technology to enable secure, transparent transactions and manage digital assets effectively in virtual worlds, supporting multi-site Industry 5.0 applications.
Creation of spatially aware applications through accurate positioning and realistic physics simulations, linking virtual experiences closely with physical industrial locations.
Implementation in transport and urban mobility to enhance resilience, safety, and sustainability. These can optimize performance and decision-making across various industrial applications, including sensor development.
Enhancement of user interaction within virtual worlds through realistic and immersive experiences, focusing on ergonomics and cost-effectiveness that support Industry 5.0 objectives.
Development aimed at augmenting worker capabilities and facilitating remote expert assistance and development management, including training and customer onboarding in industrial settings.
Proposals are expected to blend high-risk innovations with existing technologies to show how virtual worlds can add value in significant markets, supporting Industry 5.0's goals and demonstrating market viability and scalability. The innovations aim to enhance skill development, employee well-being, and knowledge retention while ensuring cost-effectiveness and resource efficiency. Ensuring solutions are interoperable is crucial for allowing seamless movement between virtual worlds and preventing monopolistic gatekeepers.
A. Enabling the smart edge
The concept of "smart edge" refers to the utilization of devices located at or near the data generation points, which facilitate the processing of this data closer to its source. This approach is evolving with a new generation of edge devices that are tailored for low-power processing, sensing, and communication. Moving intelligence closer to the data source—smart edge computing—helps overcome the limitations of centralized cloud-based processing by reducing latency, which is essential for applications needing immediate response. It also optimizes bandwidth use, enhances data privacy and security by processing data locally, and supports real-time decision-making without dependence on cloud connectivity. The market potential for smart edge solutions is growing, fueled by the broader adoption of edge computing, IoT, and AI technologies across various sectors.
Specific objectives: Focus on development of smart integrated devices for the following applications:
Edge Processing: This involves the design and integration of edge processors to minimize energy consumption and enable real-time decision-making, using technologies like low-power processors, FPGA, AI accelerators, and neuromorphic processors, with a focus on low-latency non-volatile memory and enhanced security features.
Edge Sensing and Imaging: This includes the design and integration of various sensors and imaging components such as optical sensors, Lidars, Radars, and MEMS for diverse applications like biometric, environmental, and chemical sensing.
Edge Communication: This covers the design and integration of advanced communication technologies into edge devices, including 5G and 6G, low-power wireless communication, optical connectivity, and secure networking for IoT applications.
Edge Power Management: Involves designing and integrating components that manage and optimize power usage efficiently in edge devices, utilizing technologies like wide bandgap materials for better power handling and incorporating features like dynamic power management and energy harvesting.
Integrated Smart Edge Devices: Refers to the development of highly integrated, customized edge devices using advanced packaging technologies such as System-on-Chip and System-in-Package integration, focusing on improving miniaturization, performance, and reliability of these devices.
This Challenge aims to encourage deep-tech innovations in next-generation edge and IoT semiconductor devices, which will significantly impact various sectors. In industrial automation, the technology will enhance real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated decision-making, improving productivity, reducing downtime, and enhancing safety. For mobility, it will support intelligent transportation systems and new services like automated vehicles, boosting efficiency and safety. In smart cities, innovations will enable monitoring of traffic, energy usage, and air quality, thus reducing congestion and enhancing urban life. In healthcare, the technology will facilitate remote patient monitoring and real-time medical data analysis, improving patient outcomes and making healthcare more accessible. In agriculture, it will advance precision farming to increase crop yields and reduce water usage, promoting environmental sustainability. Lastly, it will improve environmental monitoring, aiding resource management and early warning systems for natural disasters.
B. Emerging quantum technology components
This Challenge is dedicated to promoting advancements in quantum information processing components.
Specific objectives: Encourage cutting-edge innovations with a strong potential for development in several areas:
Full stack fault-tolerant quantum computing that enhances performance, simplifies the integration of Quantum Processing Units (QPU) with control electronics, features scalable control systems capable of handling tens of thousands of qubits for significant practical applications, and advances software development.
Quantum sensing components to function in real/harsh environment
Quantum communication devices.
This Challenge is aimed at advancing the production of food using precision fermentation and algae, effectively separating food production from reliance on soil and external environmental factors.
Specific objectives: This Challenge aims to foster the development of sustainable and nutritious food production using precision fermentation and algae. The innovations required should not only refine current technologies but also introduce groundbreaking production methods that are energy-efficient, resource-conservative, and produce low-emission foods essential for a healthy diet. Specifically, this challenge seeks to develop and scale up interdisciplinary solutions in two main areas: fermentation systems based on bacteria, yeast, or fungi, and innovative aquaculture systems utilizing both macro and micro-algae.
The focus is on enhancing the sustainability, efficiency, and resilience of Europe's food supply chain by reducing reliance on soil and minimizing environmental impacts such as water pollution. It encourages groundbreaking technological advancements that could disrupt current markets, aiming to secure new food sources that also support environmental preservation and biodiversity. Addressing climate change challenges, such as biodiversity loss and pollution, is essential, and the initiative seeks to strengthen EU technological independence and leadership in scalable food production technologies that benefit both European consumers and those globally. Additionally, the development of novel foods and processes is anticipated to offer healthier alternatives, potentially reducing the prevalence of food-related health issues among the general population.
This challenge focuses on the development of mAbs-based therapeutics against new variants of emerging pathogens of high concern.

Specific objectives: focus on several key areas:
Developing broad-spectrum mAbs-based therapies that can target multiple pathogens.
Enhancing the effectiveness of mAbs therapies, including addressing variations in treatment response among individuals.
Simplifying the clinical administration of mAbs for outpatients with mild symptoms, especially in scenarios where hospitals are overwhelmed or patients exhibit hypersensitivity to treatments.
Innovating rapid production techniques for mAbs to shorten lead times and ensure quick availability in case of an outbreak.
Creating new technologies for administering mAbs that could extend the antibody’s half-life or involve injecting mRNA to produce the antibody.
These initiatives are aimed at ensuring a swift and effective response to public health emergencies, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing the scalability of treatments.
This challenge focuses on enhancing the EU's energy strategic autonomy by scaling up renewable energy sources (RES) and their supply chains. It aims to reduce the EU's dependency on imported components, including critical raw materials (CRM), aligning with the goals of the Net-zero industry and Critical Raw Materials Acts.

Specific objectives:
Increasing the production of RES systems that generate heat and electricity from renewable sources, applicable at various scales (from power plants to small-scale installations), locations (onshore or offshore), and for different uses (stationary and mobility).
Expanding technologies for the exploration, mining, and processing of materials used in RES, explicitly excluding CRMs.
Enhancing technologies for the recycling or reuse of RES components into viable materials and components.
These efforts emphasize developing technologies without relying on CRMs or ensuring maximum recyclability and reusability to support a circular economy. Additionally, minimizing the environmental footprint through life-cycle analysis, including assessing cost and social impacts, is a critical component of this challenge.
Budget, timeline and eligibility criteria
The total budget for EIC Accelerator Challenge is 300M€, 50M€ for each Challenge. For the Challenge n°3, at least 30% will be allocated to A and at least 30% for B thematic. The call deadline for submitting the full proposal is 3 October 2024.
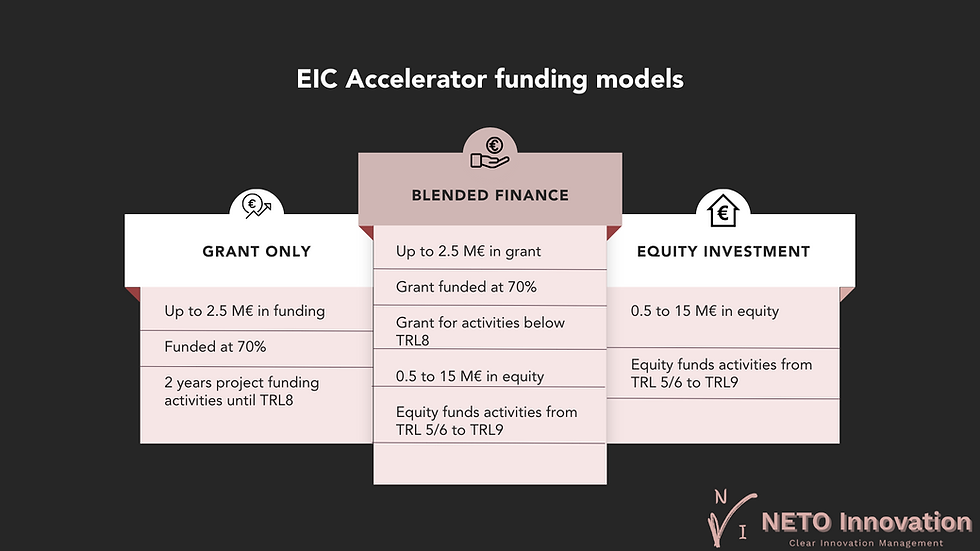
For more information about the EIC Accelerator funding scheme, please see our previous blog: Boosting innovation: How the EIC Accelerator is empowering SMEs and start-ups.
How can NETO Innovation support you?
As a result of our large network and project writing expertise, we can assist you with:
Finding the right partners in the participating countries. NETO Innovation has access to a wide range of partners, both private and public. Our team has the necessary skills and experience to match you with the best possible partners for your project. We can also ensure that the project is written in a way that meets your specific requirements and specifications.
Supporting you in writing the project application. Our team has experience in writing for a variety of partners, across different sectors and disciplines. We are familiar with the requirements of various funding bodies and can provide you advice on how to make your project application stand out from the rest. We also have experience in writing for a range of audiences, so you can be sure that your project application is written with clarity and precision.
Fill in the online application and submit the proposal. With NETO Innovation’s team you can be assured that your project application is clear, concise, compelling, and submitted on time.
Interested in the EIC Accelerator Challenges call? Does writing grant applications seem overwhelming to you? Feel free to contact the NETO Innovation team to find out how we can support you and ease your innovation funding process. We can also provide you with more information about the possible budgets, selection criteria, and evaluation process. So, hurry up and contact our team here.
Follow us on our social media channels for more informative content like this.




Kommentarer